Sampling Guidance
2024-12-27Bettersizer
Particle size testing is a process that characterizes the particle size distribution of many substances by testing and analyzing a small number of samples. Representative and convincing particle size test results are inseparable from a reasonable sampling process. Accordingly, the sampling is the first and most important part of particle size testing. The sampling is a process of obtaining “laboratory samples (10n grams)” from “large amounts of samples (10n kg)”, and then obtaining “test samples (10n mg)” from “laboratory samples”.
1) Acquisition of Laboratory Samples from the Process Stream
The best method of sampling from the process is to remove the sample from a flowing powder stream rather than from a static pile like a silo or a drum. Suppose the only possibility is a static powder pile. In that case, samples should be removed from different positions and different depths in the pile or drum, which will be mixed to obtain a representative laboratory sample.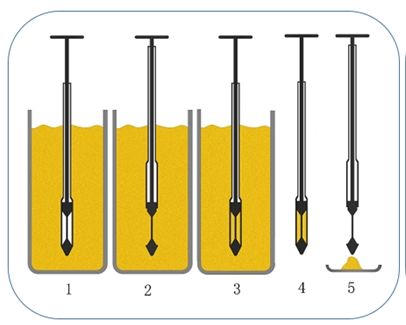
2) Acquisition of Test Sample
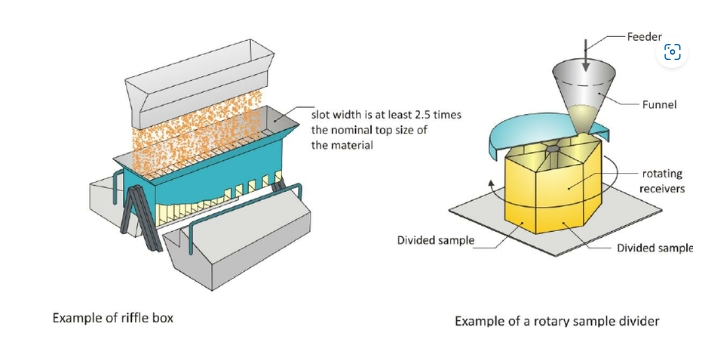
Users can use a spinning riffler to acquire a representative test sample from this laboratory sample. A spinning riffler is a device that divides the laboratory sample into many fractions, whose characteristic composition corresponds exactly to that of the original laboratory sample. Each fraction can be used as a test sample. If the fraction is excessive, it needs to be handled by the spinning riffler again to make sure that the entire subsample will be used for a single measurement. A spoon can be used to sample from the laboratory sample if the sample is held in typically, a solid glass jar with a screw cap. However, the jar must be at least 30% empty to allow the rest of the powder in the jar (70% or less) to be tumbled for homogenization. The tumbling should be done 7 times in succession before taking the sample from the jar. The jar must never be shaken as vibration creates stratification causing the user to sample coarse particles from the top of the jar and this will not be representative and will lead to a test producing a larger particle size analysis.