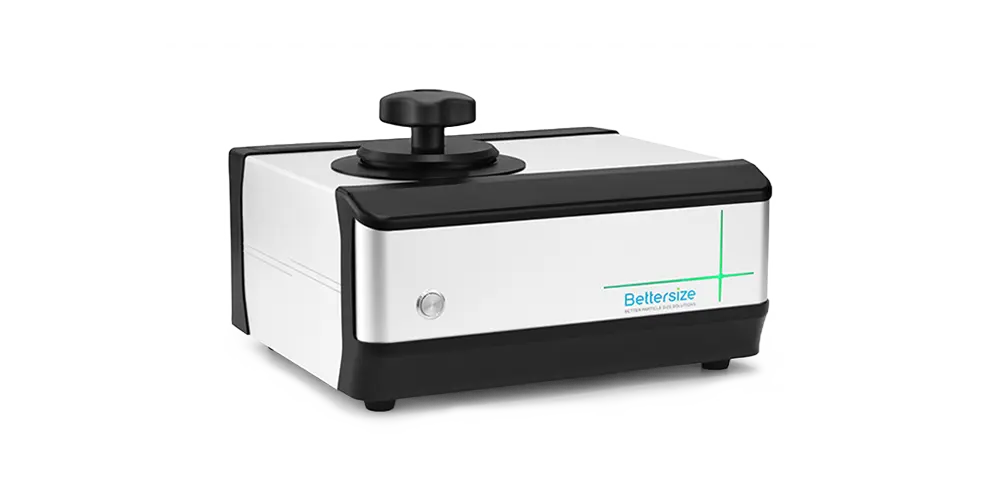
연마재
Bettersize 장비를 통한 실리콘 카바이드, 가넷, 다이아몬드, 알루미늄 산화물 및 코런덤의 입자 크기 분포 및 입자 형태 분석
연마재는 마찰과 문질러서 표면을 감소시키는 물질로, 화학 기계적 연마, DVR/CD 디스크, 샌드페이퍼, 연삭 휠, 절단 휠, 바닥 미끄럼 방지, 밀링, 치약, 주방 및 욕실 세제 등 다양한 분야에서 널리 사용됩니다.
이처럼 연마재는 제조 산업의 중요한 "이빨" 역할을 합니다. 실리콘 카바이드 분말은 주로 다중 와이어 절단 기계에서 사용되는 밀링 물질로, 그 입자 형태와 크기는 실리콘 웨이퍼의 표면 매끄러움과 절단 효율성에 중요한 영향을 미칩니다. 실리콘 카바이드 분말은 실리콘 웨이퍼 절단의 핵심 재료입니다. 적절한 입자 형태를 가진 분말은 절단 후 실리콘 웨이퍼의 표면을 매끄럽게 만들며, 입자 크기 분포를 좁히고 코너 각도를 더욱 뾰족하게 하면 절단 효율을 높일 수 있습니다.
연마재의 3가지 중요한 특성
연마재로 사용되는 물질의 기능을 결정하는 주요 특성은 경도, 예리함, 내구성입니다. 경도와 예리함은 표면을 감소시키고, 내구성은 연마작용을 견디는 능력에 해당합니다. 표면을 처리할 때는 선택한 연마재의 경도가 처리될 표면의 경도보다 낮아야 합니다. 고경도는 연삭, 연마 또는 표면 제거에 필요합니다.
연마재로 사용되는 주요 재료는 가넷, 다이아몬드, 실리콘 카바이드, 알루미늄 산화물입니다.
입자 크기와 형태의 중요성
입자 크기는 연마재의 적절한 선택과 사용에 있어 중요한 요소입니다. 전통적으로 입자 크기는 체를 이용하여 측정했지만, 체 측정은 매우 작은 입자를 측정하는 데 한계가 있으며, 입자의 가장 큰 차원만을 측정하기 때문에 형태에 편향이 있을 수 있습니다. 연마재의 입자 크기는 6mm에서 6μm까지 다양합니다.
입자 형태는 연마 작업의 효율성에 중요한 영향을 미칩니다. 예리함은 한 물질이 다른 표면에서 물질을 제거하는 능력을 나타내는 지표입니다. 입자 표면의 거칠기(asperity)는 처리 표면의 마모 속도와 연마재의 효율성에 영향을 미칩니다. 일정 크기 이하로 입자가 작아지면 마모 속도가 감소합니다. 예리함은 SPQ(Spike Parameter Quadratic) 계산과 같은 절차로 측정할 수 있지만, Bettersize의 DIA 시스템을 사용하면 입자의 각도를 측정할 수 있어 Krumbein 방법보다 훨씬 우수한 결과를 제공합니다.
각도 측정과 예리함
각도(Angularity)는 입자의 예리함을 평가하는 데 더 나은 지표가 될 수 있습니다. 이는 입자의 모든 뾰족한 모서리를 고려하기 때문입니다. 반면, Krumbein 방법은 입자의 가장 큰 차원만을 고려하는 방식으로, 입자의 예리함을 정확히 반영하지 못할 수 있습니다.
Bettersize DIA 동적 이미지 분석 시스템을 통한 입자 분석
Bettersize의 동적 이미지 분석 시스템은 입자의 형태를 정밀하게 분석할 수 있어, 연마재의 효율성을 평가하고, 연마 공정에서 최적의 성능을 발휘하도록 도와줍니다. 이 시스템은 입자의 각도와 예리함을 측정함으로써 연마재의 품질을 보장하고, 최적화된 제조 공정을 제공합니다.
Bettersize의 고급 분석 장비는 실리콘 카바이드, 가넷, 다이아몬드, 알루미늄 산화물, 코런덤 등의 연마재에 대한 입자 크기 분포와 입자 형태 분석을 제공하여, 다양한 산업 분야에서 효율적이고 정밀한 연마 작업을 지원합니다.
Citations
- Bettersizer 2600
Functional redundancy as an indicator for evaluating functional diversity of macrobenthos under the mussel raft farm near Gouqi Island
DOI: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2023.740024 Read ArticleZhejiang Ocean University | 2024Biological traits analysis (BTA) helps to evaluate the effects of different environmental variables on the traits-based functional composition of macrobenthos. However, research on functional traits of macrobenthos under mussel farming is limited. We investigated the spatial and temporal response of the benthic system in terms of taxonomic and functional diversity to environmental variables of farming and natural stressors resulting from suspended mussel farming near Gouqi Island of eastern China Sea. The functional traits of macrobenthic assemblages under mussel farming were characterized by “medium adult body size”, “vermiform body form”, “high flexibility”, “infauna”, “semi-motile”, “gonochoristic”, “surface deposit-feeders”, “carnivores”, “semi-motile burrowers”, and “tube-dwellers”. Functional redundancy was stable in response to mussel farming stresses among seasons, whereas species diversity showed efficient to evaluate natural variables. Functional diversity was significantly affected by farming stressors rather than natural variables, Further analysis using multivariate methods together with continuous monitoring were highlighted to evaluate the impacts of mussel farming. Our results reinforce the importance of macrobenthic species and functional traits analysis to evaluate human stresses driven impacts in offshore ecosystems. By analysing the environmental variables with different sources, independently, we concluded the main effects of human pressures on macrobenthic community. Such distinction could be particularly effective to isolate variable environmental descriptors and evaluate their effects on functional diversity, making the current approach promising for the evaluation of ecological effects of anthropogenic stressors in aquaculture areas. - Bettersizer 2600
Degradation characteristics and utilization strategies of a covalent bonded resin-based solid amine during capturing CO2 from flue gas
DOI: 10.1016/j.seppur.2023.125621 Read ArticleChina University of Petroleum | 2024In this study, various types of degradation as well as attrition which are possibly encountered in a circulating fluidized bed temperature swing adsorption (CFB-TSA) process, were conducted experimentally to evaluate the stability of a resin-based solid amine sorbent. Other characterizations methods, such as elemental analysis (EA), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) etc. were applied to further reveal the degradation mechanisms. The results showed that thermal degradation occurs from 140–160 °C due to the decomposition of amine group. The CO2-induced degradation occurs from a higher temperature of 160–180 °C accompanied by the production of urea. Hydrothermal stability is good below 130 °C, but the ionic impurities in steam crystalized on particle surface can accelerate the degradation. Oxidative degradation is the most harmful, which starts at a lower temperature of 70–80 °C with the formation of aldehyde. The existence of H2O in atmosphere can alleviate the oxidative and CO2-induced degradations. The employed sorbent has a very low attrition index of 0.05, which is 1–2 orders lower than typical commercial fluidized bed catalysts. Based on the results of stability evaluation, some design suggestions for proper utilization of this sorbent or other similar resin-based sorbents have been provided in an industrial CFB-TSA process.
- Bettersizer 2600
De-branching of starch molecules enhanced the complexation with chitosan and its potential utilization for delivering hydrophobic compounds
DOI: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2023.109498 Read ArticleShihezi University | 2024The current study aimed to prepare the complexes between debranched-waxy corn starch and chitosan polymers (DBS-CS), and then investigated their corresponding structural characteristics, rheological property and potent application in Pickering emulsion. The results indicated that the existence of chitosan significantly inhibited starch short-range molecular rearrangement for all DBS-CS samples, which was manipulated by both debranching treatment and chitosan content. Interestingly, this is the first study to reveal that the outstanding peak at 1.8 ppm in 1H NMR spectrum for sample DBS-CS was gradually shifted towards a lower-field region following an increased chitosan content. Moreover, the debranching treatment shifted the crystallinity pattern from A-type to B-type and the relative crystallinity of DBS-CS decreased gradually with the increased content of CS. All samples had a pseudoplastic fluid and shear-thinning behavior with an enhanced shear resistance following the complexation. The DBS-CS was applied in a Pickering emulsion for showing a greater emulsifying stability and a lower gel strength than native NS-CS prepared emulsion. Importantly, the encapsulation ability of curcumin in the DBS-CS emulsion was significantly improved, followed by an increase of 15.45% for its corresponding bioavailability compared to the control. Therefore, this study might highlight a potential carrier for delivering the bioactive substances in a green pattern. - Bettersizer 2600
Heat-induced aggregation behavior of wheat gluten after adding citrus pectin with different esterification degree
DOI: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2023.109420 Read ArticleGansu Agricultural University | 2024Wheat gluten aggregation during heat treatment is beneficial to the final quality of gluten-based products. Exogenous pectin can affect gluten aggregation. However, the effect of pectin with different degrees of esterification on the heat-induced aggregation behavior of gluten and its possible mechanism are still unclear. Thus, the heat-induced aggregation behavior of gluten after adding pectin with different esterification degree was studied in this study. When the temperature was raised from 25 °C to 95 °C, pectin affected gluten aggregation and was related to the degree of esterification. Specifically, the results of rheological properties and particle size indicated that low-ester pectin improved the viscoelasticity of gluten and promoted gluten aggregation. Thermal properties revealed that enthalpy of gluten added with low-ester pectin (37%) increased from 92.96 J/g to 95.40 J/g during heating process. Structurally, the fluorescence intensity and surface hydrophobicity of gluten added with low-ester pectin (37%) were lower than those added with high-ester pectin (73%). In addition, low-ester pectin (37%) significantly increased the disulfide bond content (from 15.31 μmol/g to 18.06 μmol/g) and maintained β-sheet content of gluten compared with gluten alone at 95 °C, indicating that low-ester pectin was more likely to induce gluten aggregation. However, scanning electron microscope showed that the gluten added with low-ester pectin (46%) exhibited a denser network structure at 95 °C than that added with low-ester pectin (37%). These results will provide a theoretical base for the regulation of gluten aggregation and the quality of gluten-based products by pectin with different esterification degree.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 84