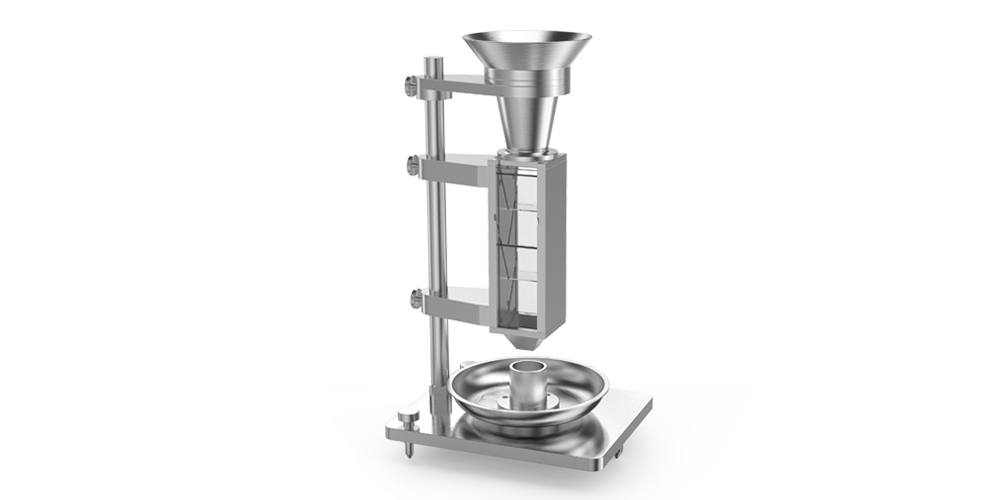
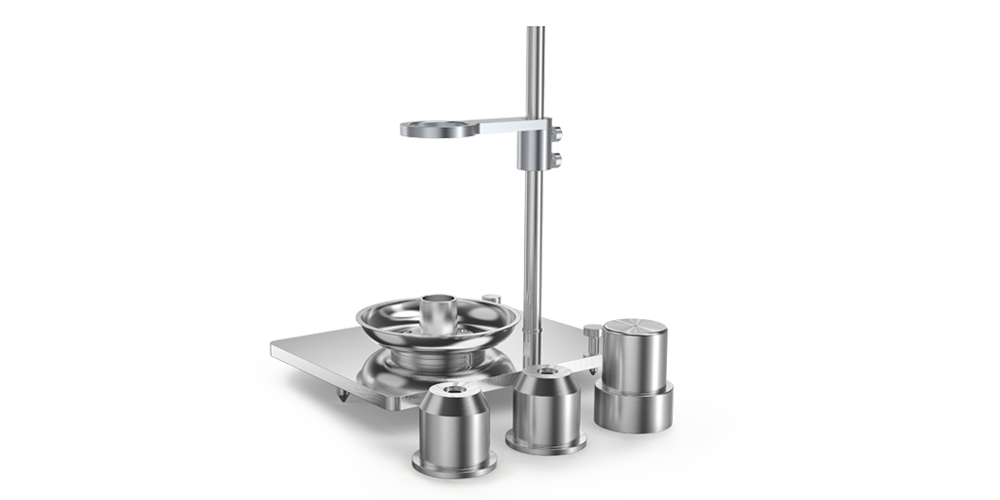
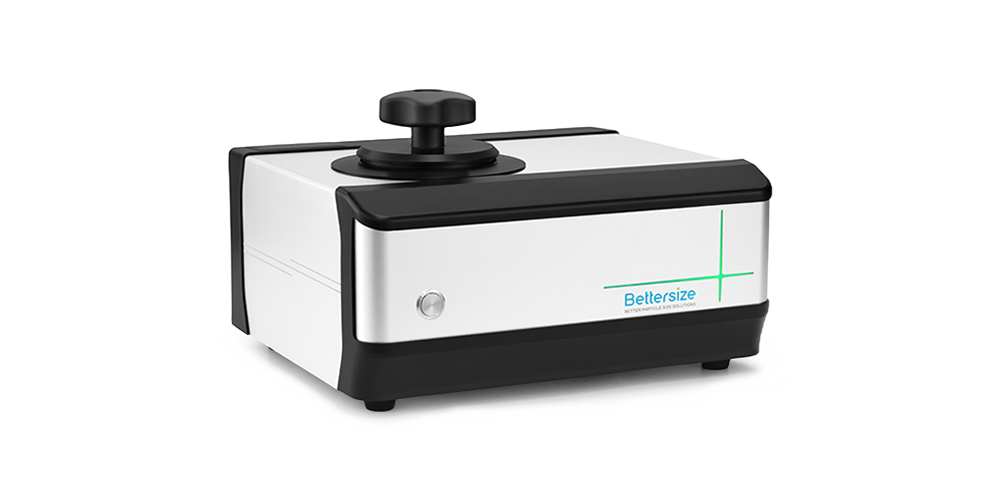
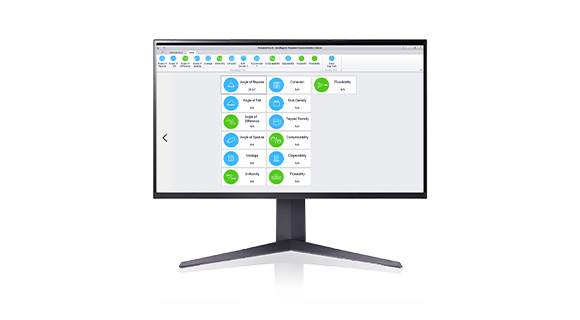
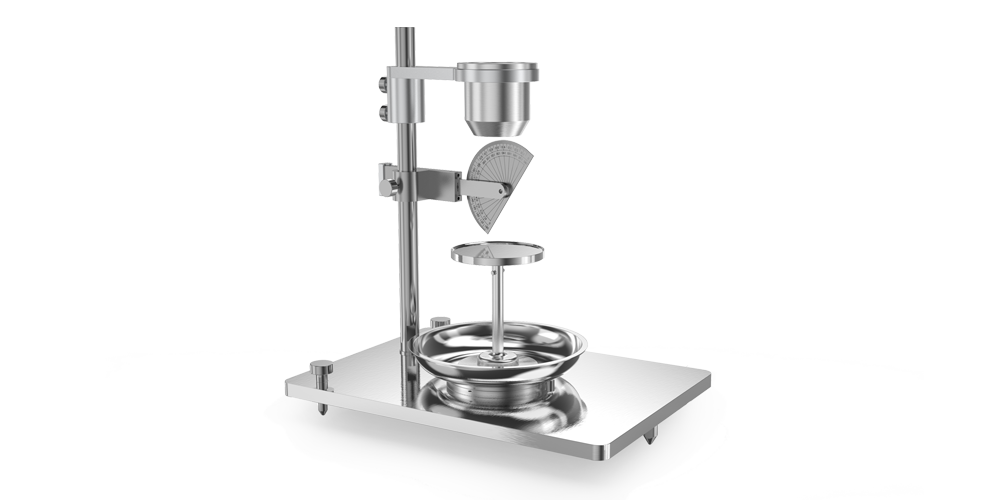
PowderPro A1粉体物性総合試験機は、Wi-Fiによる端末制御、自動画像処理、3D回転振動技術によるタップ密度測定など、多くのハイエンドな技術を搭載しています。迅速、簡単、かつ正確に粉体の物理的性質を測定することができます。スマートなPowderPro A1は粉体材料の理解や研究に役立つ、必要不可欠な測定機です。
機能と利点
- ● 高解像度CCDカメラを用いた自動角度測定
- ● 一体型設計
- ● 高い操作性
- ● 計量データの転送
- ● 自動制御技術
- ● 自動画像処理技術
ビデオ
What is angle of repose? Why and how do we measure it? 
Flowability Calculation of Powder Materials Using PowderPro A1 
Cohesion & Uniformity Measurement and Calculation of Powder Materials Using PowderPro A1 
Tapped Density and Compressibility Measurement of Powder Materials Using PowderPro A1 
Bulk Density Testing of Non-metallic Powder Materials with PowderPro A1 
Angle of Spatula Measurement of Powder Materials with PowderPro A1 
Angle of Repose, Angle of Fall & Angle of Difference Testing of Powder Materials with PowderPro A1 
PowderPro A1 Overview | Automatic Powder Characteristics Tester 
概要
PowderPro A1粉体物性総合試験機の装置概要
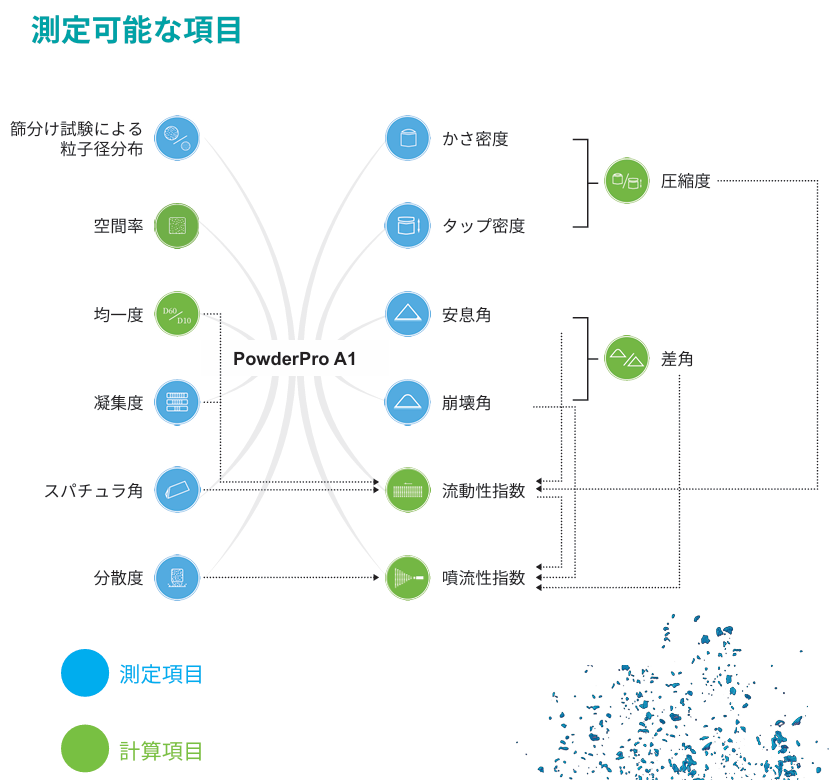
1. 測定可能な項目
|
1) 測定項目
|
2) 計算項目
|
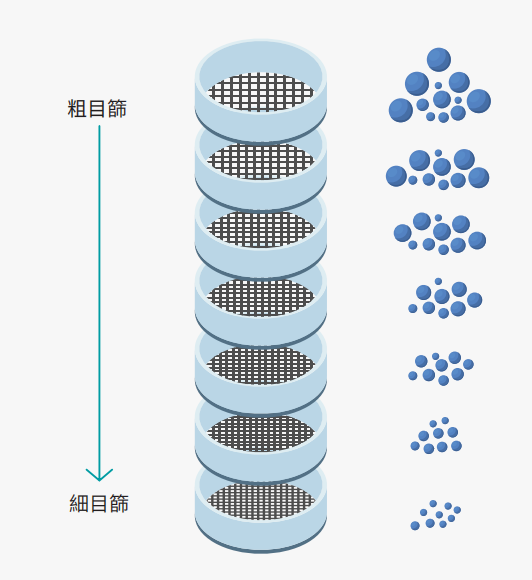
2. 篩分け試験による粒子径分布
PowderPro A1 は、粒度分布測定の一手法であるふるい分け試験を手軽に行える機能を搭載しています。この機能により、粉体の流動性や圧縮性などの重要な特性を迅速かつ正確に評価することができ、製薬、地質学、冶金学、建築業界における品質管理や研究開発に欠かせないツールです。 さらに、ふるい上の粉体の重量を正確に測定するために、天秤と直接連携できる設計となっており、測定プロセスにおける人的ミスを最小限に抑えます。これにより、より信頼性の高い結果が得られ、 品質管理の精度が向上します。操作性に優れたデザインとコストパフォーマンスを両立したPowderPro A1は、正確な粒度分布測定を実現し、製品品質の向上に貢献する理想的なソリューションです。
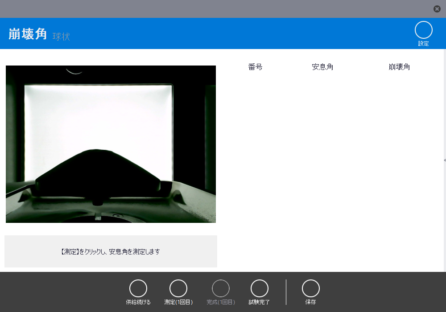
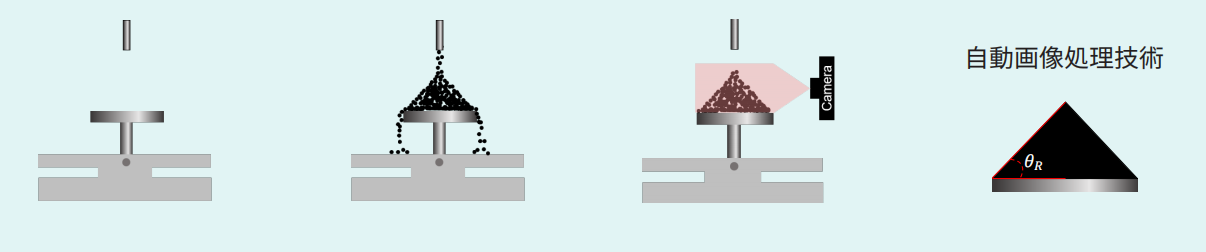
3. 高解像度カメラを用いた自動角度測定
高解像度CCDカメラを用いて粉体画像を撮影します。高度な画像処理技術により明るい環境下においても安定した角度測定を可能とし、安息角、崩壊角、スパチュラ角などを高精度で再現性良く取得出来ます。
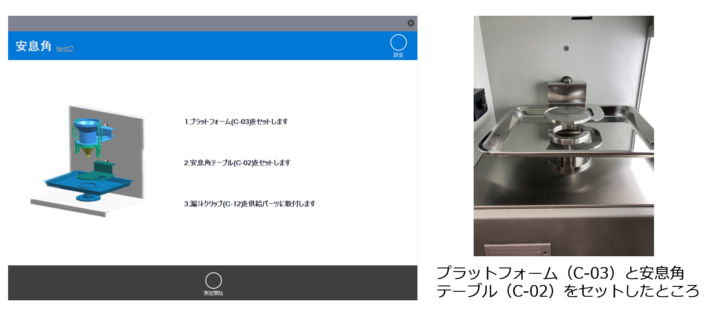
4. 特許取得の回転振動技術
振動中、シリンダーは均一な回転状態にあるため、粉体の水平面が保証され、測定精度が向上します。
5. 高い操作性
PC専用ソフトの画面に表示される操作説明に沿って行うことで、初めての方でも簡単に測定が行えます。内蔵されたミニプリンタから試験結果をプリント可能で、作業効率向上にも力を入れています。
6. 規格準拠
- ISO 3953:2011
- USP 44 - NF 39 <616>
- Ph. Eur.10.0 04/2019:20934
7. 計量データの転送
付属の電子天びんから PowderPro A1 へ計量データが送られ、計量データは専用解析ソフトに記録されるため簡単に作業できます。

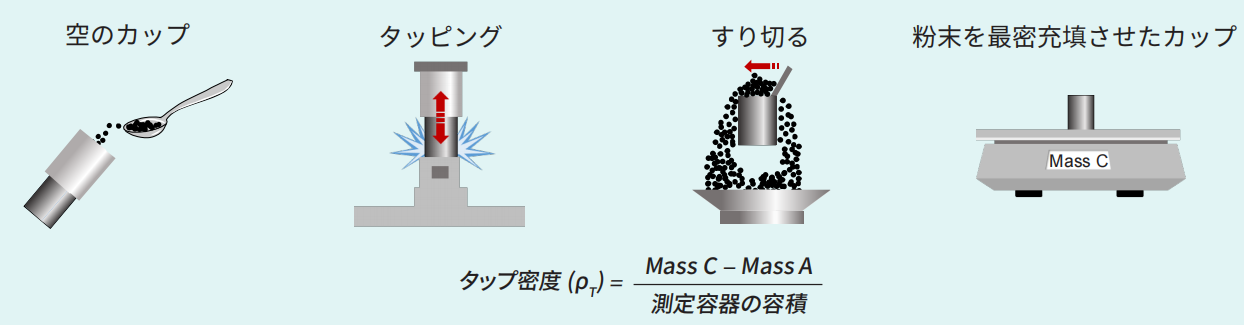
8. タップ密度測定
タップ密度は、可変周波数と回転振動技術の組み合わせにより測定します。振動回数は毎分50~300回の範囲で調整可能で、落下高さは3mmまたは14mmを選択できます。振動中、シリンダーは均一な回転状態に保たれ、粉体表面が水平になることで測定精度が向上します。
- 安息角の測定
- タップ密度の測定
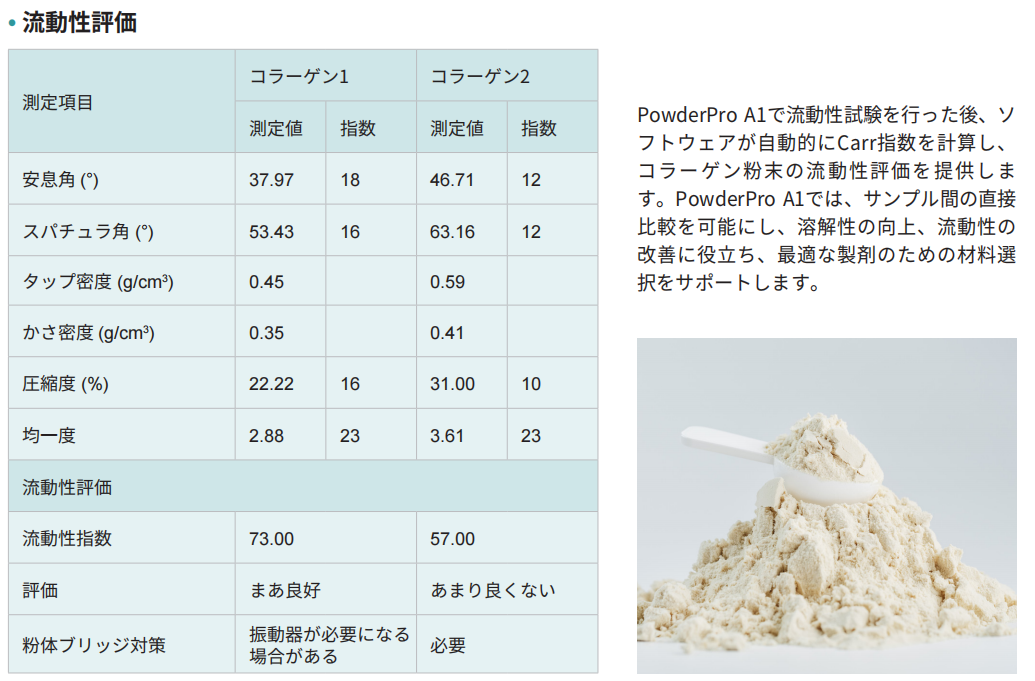
9. 測定例:たんぱく質補給粉末のカー指数と流動性の洞察
PowderPro A1は、流動性を表わすCarr指数を計算し、粉末の流動性評価を行うことで、プロテインパウダーの新製品 開発や研究においてお役に立ちます。
Citations
- Bettersizer 2600
Functional redundancy as an indicator for evaluating functional diversity of macrobenthos under the mussel raft farm near Gouqi Island
DOI: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2023.740024 Read ArticleZhejiang Ocean University | 2024Biological traits analysis (BTA) helps to evaluate the effects of different environmental variables on the traits-based functional composition of macrobenthos. However, research on functional traits of macrobenthos under mussel farming is limited. We investigated the spatial and temporal response of the benthic system in terms of taxonomic and functional diversity to environmental variables of farming and natural stressors resulting from suspended mussel farming near Gouqi Island of eastern China Sea. The functional traits of macrobenthic assemblages under mussel farming were characterized by “medium adult body size”, “vermiform body form”, “high flexibility”, “infauna”, “semi-motile”, “gonochoristic”, “surface deposit-feeders”, “carnivores”, “semi-motile burrowers”, and “tube-dwellers”. Functional redundancy was stable in response to mussel farming stresses among seasons, whereas species diversity showed efficient to evaluate natural variables. Functional diversity was significantly affected by farming stressors rather than natural variables, Further analysis using multivariate methods together with continuous monitoring were highlighted to evaluate the impacts of mussel farming. Our results reinforce the importance of macrobenthic species and functional traits analysis to evaluate human stresses driven impacts in offshore ecosystems. By analysing the environmental variables with different sources, independently, we concluded the main effects of human pressures on macrobenthic community. Such distinction could be particularly effective to isolate variable environmental descriptors and evaluate their effects on functional diversity, making the current approach promising for the evaluation of ecological effects of anthropogenic stressors in aquaculture areas. - Bettersizer 2600
Degradation characteristics and utilization strategies of a covalent bonded resin-based solid amine during capturing CO2 from flue gas
DOI: 10.1016/j.seppur.2023.125621 Read ArticleChina University of Petroleum | 2024In this study, various types of degradation as well as attrition which are possibly encountered in a circulating fluidized bed temperature swing adsorption (CFB-TSA) process, were conducted experimentally to evaluate the stability of a resin-based solid amine sorbent. Other characterizations methods, such as elemental analysis (EA), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) etc. were applied to further reveal the degradation mechanisms. The results showed that thermal degradation occurs from 140–160 °C due to the decomposition of amine group. The CO2-induced degradation occurs from a higher temperature of 160–180 °C accompanied by the production of urea. Hydrothermal stability is good below 130 °C, but the ionic impurities in steam crystalized on particle surface can accelerate the degradation. Oxidative degradation is the most harmful, which starts at a lower temperature of 70–80 °C with the formation of aldehyde. The existence of H2O in atmosphere can alleviate the oxidative and CO2-induced degradations. The employed sorbent has a very low attrition index of 0.05, which is 1–2 orders lower than typical commercial fluidized bed catalysts. Based on the results of stability evaluation, some design suggestions for proper utilization of this sorbent or other similar resin-based sorbents have been provided in an industrial CFB-TSA process.
- Bettersizer 2600
De-branching of starch molecules enhanced the complexation with chitosan and its potential utilization for delivering hydrophobic compounds
DOI: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2023.109498 Read ArticleShihezi University | 2024The current study aimed to prepare the complexes between debranched-waxy corn starch and chitosan polymers (DBS-CS), and then investigated their corresponding structural characteristics, rheological property and potent application in Pickering emulsion. The results indicated that the existence of chitosan significantly inhibited starch short-range molecular rearrangement for all DBS-CS samples, which was manipulated by both debranching treatment and chitosan content. Interestingly, this is the first study to reveal that the outstanding peak at 1.8 ppm in 1H NMR spectrum for sample DBS-CS was gradually shifted towards a lower-field region following an increased chitosan content. Moreover, the debranching treatment shifted the crystallinity pattern from A-type to B-type and the relative crystallinity of DBS-CS decreased gradually with the increased content of CS. All samples had a pseudoplastic fluid and shear-thinning behavior with an enhanced shear resistance following the complexation. The DBS-CS was applied in a Pickering emulsion for showing a greater emulsifying stability and a lower gel strength than native NS-CS prepared emulsion. Importantly, the encapsulation ability of curcumin in the DBS-CS emulsion was significantly improved, followed by an increase of 15.45% for its corresponding bioavailability compared to the control. Therefore, this study might highlight a potential carrier for delivering the bioactive substances in a green pattern. - Bettersizer 2600
Heat-induced aggregation behavior of wheat gluten after adding citrus pectin with different esterification degree
DOI: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2023.109420 Read ArticleGansu Agricultural University | 2024Wheat gluten aggregation during heat treatment is beneficial to the final quality of gluten-based products. Exogenous pectin can affect gluten aggregation. However, the effect of pectin with different degrees of esterification on the heat-induced aggregation behavior of gluten and its possible mechanism are still unclear. Thus, the heat-induced aggregation behavior of gluten after adding pectin with different esterification degree was studied in this study. When the temperature was raised from 25 °C to 95 °C, pectin affected gluten aggregation and was related to the degree of esterification. Specifically, the results of rheological properties and particle size indicated that low-ester pectin improved the viscoelasticity of gluten and promoted gluten aggregation. Thermal properties revealed that enthalpy of gluten added with low-ester pectin (37%) increased from 92.96 J/g to 95.40 J/g during heating process. Structurally, the fluorescence intensity and surface hydrophobicity of gluten added with low-ester pectin (37%) were lower than those added with high-ester pectin (73%). In addition, low-ester pectin (37%) significantly increased the disulfide bond content (from 15.31 μmol/g to 18.06 μmol/g) and maintained β-sheet content of gluten compared with gluten alone at 95 °C, indicating that low-ester pectin was more likely to induce gluten aggregation. However, scanning electron microscope showed that the gluten added with low-ester pectin (46%) exhibited a denser network structure at 95 °C than that added with low-ester pectin (37%). These results will provide a theoretical base for the regulation of gluten aggregation and the quality of gluten-based products by pectin with different esterification degree.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 84