BeVision S1は、0.3〜4,500μmの範囲における粒子径および形状を簡便かつ高精度に測定・分析するための優れたソリューションを提供します。操作が簡単でありながら、信頼性と精度を兼ね備えており、さまざまな分析ニーズに対応可能です。BeVisionソフトウェアは、34種類の粒子径および形状パラメータを提供し、データを総合的に整理して粒子の完全な検証をサポートします。これにより、粒子の詳細な特性評価が可能となり、分析結果を直感的に理解することができます。さらに、BeVision S1は、単独の粒子サイズおよび形状分析装置としてだけでなく、レーザー回折式粒子解析装置と組み合わせて使用することも可能です。これにより、補助的な分析や検証を行い、信頼性の高いデータを提供します。
機能と利点
- ● 測定範囲: 0.3 ~ 4,500 μm
- ● 乾式および湿式測定対応
- ● 34種類の粒子径および形状パラメータを提供
- ● 特定の用途にオプション顕微鏡を選択可能
- ● 強力なソフトウェアで作業の効率化
- ● カスタマイズ可能なレポート機能
- ● ISO 9276-6準拠の測定結果
ビデオ
What is Image Analysis? Fundamentals of BeVision Series 
How to Install and Operate BeVision S1 
Overview of BeVision Series | Precision in Particle Vision 
概要
装置特徴
画像解析とは
製品仕様
BT-910 乾燥粉末分散モジュール
 BeVision S1:クラシックな粒子径・粒子形状解析装置
BeVision S1:クラシックな粒子径・粒子形状解析装置
BeVision S1は、0.3〜4,500μmの範囲における粒子径および粒子形状を簡便かつ高精度に測定・分析するための優れたソリューションを提供します。操作が簡単でありながら、信頼性と精度を兼ね備えており、さまざまな分析ニーズに対応可能です。
BeVisionソフトウェアは、34種類の粒子径および形状パラメータを提供し、データを総合的に整理して粒子の完全な検証をサポートします。これにより、粒子の詳細な特性評価が可能となり、分析結果を直感的に理解することができます。
さらに、BeVision S1は、単独の粒子径および形状分析装置としてだけでなく、レーザー回折式粒子解析装置と組み合わせて使用することも可能です。これにより、補助的な分析や検証を行い、より精緻で信頼性の高いデータを提供します。
1. 画像解析法を採用する理由は何か?
- 簡便なプロセス: 画像解析法は、粒子の画像をキャプチャして粒子を特定し、サイズと形状を迅速に測定します。各ステップはシンプルであり、明確な手順で解析が進行します。
- 形状解析の優位性: 画像解析法では、粒子を直視することで、粒子の大きさだけでなく、形状も詳細に評価することができます。
- 百聞は一見に如かず: 画像解析法では、各粒子のサイズや形状を詳細に測定し、それらを統計的にまとめて分析します。この方法により、粒子径や形状の分布に関する精度の高い情報を提供することが可能です。
2. 静的画像解析法を選ぶ理由は何か?
- 高精度な視覚情報: 静的画像解析法では、高解像度カメラと精密顕微鏡を使用して、粒子の鮮明な画像を取得します。この技術により、非常に小さな粒子でも明確に視覚化し、詳細な分析が可能です。
- 微小粒子の検出能力: 静的画像解析法は、微小粒子を高感度で検出でき、従来の方法では捉えきれない微細な粒子も正確に解析することができます。
- サンプル量の少なさ: この手法では、少量のサンプルでの測定が可能です。数滴のエマルションや数マイクログラムの粉末で経済的に粒子解析を行うことができます。
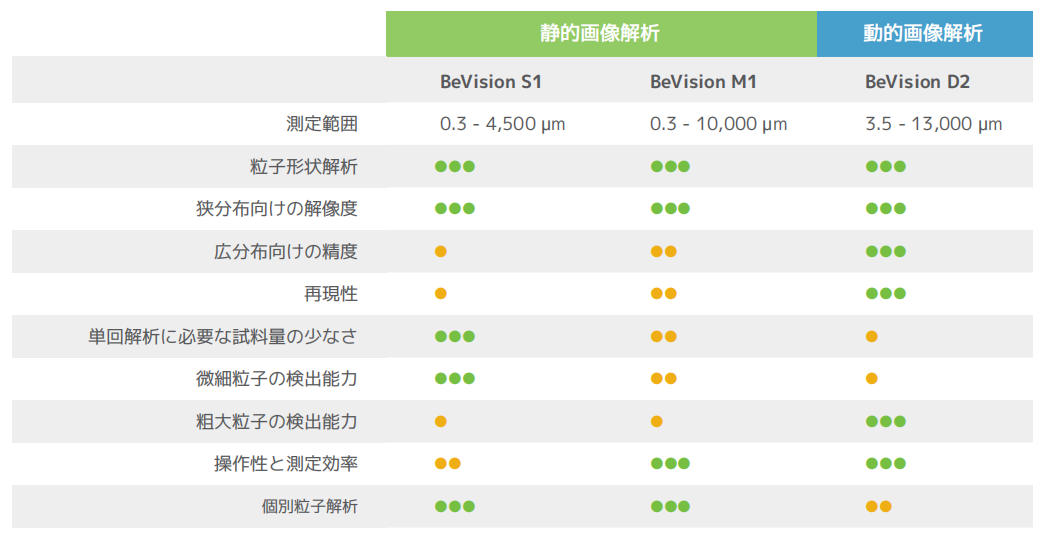
3. BeVisionシリーズ一覧
4. 34種の粒子径と形状パラメータを提供

4.1 粒子径関連パラメータ
等価径(Equivalent diameters):
-
- 投影面積円相当径
- 投影周長円相当径
フェレー径(Feret diameters):
-
- フェレー最大径、フェレー最小径、XLF
- フェレー最大径、フェレー最小径、XLF
マーチン径(Martin diameters):
-
- マーチン最大径、マーチン最小径
- マーチン最大径、マーチン最小径
ルジャンドルの慣性楕円(Legendre ellipse):
-
- 長軸、短軸
4.2 粒子形状関連パラメータ
2方向の解析:
-
- アスペクト比(aspect ratio)
- 縦横比(L/W ratio)
- 楕円比(ellipse ratio)
円形度と矩形度:
-
- 円形度(Circularity、11のアルゴリズムを選択可能)
- 不規則性(irregularity)
- コンパクト度(compactness)
- エクステント(extent)
- かさ指数(box ratio)
輪郭の凹凸:
-
- 凹み度(Concavity)
- 凸度(convexity)
- 充実度(solidity)
細長い粒子:
-
- 長短度(Elongation)
- 直線度(straightness)
5.測定事例
ガラスビーズ
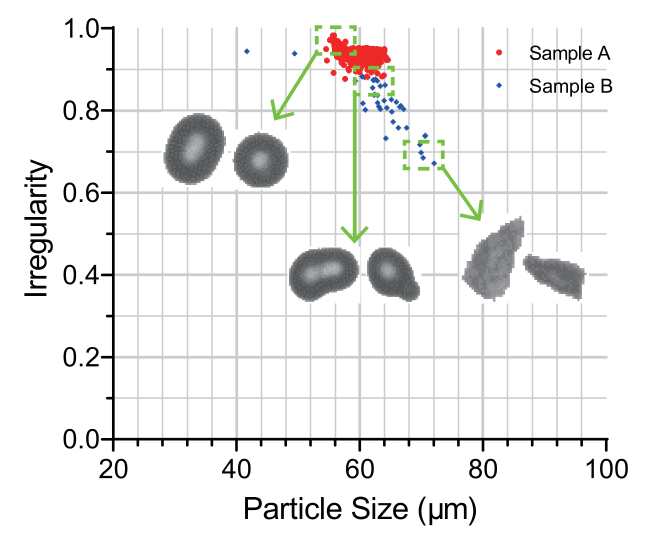
ガラスビーズは、建設、交通標識塗料、サンドブラストなどのさまざまな産業で広く利用されており、特にその粒度および形状が製品の性能に重要な影響を与えます。例えば、ガラスビーズの研磨効果は粒子の均一性や形状の不規則性によって決まります。BeVision S1は、粒度と形状の両方を高精度で同時に測定できるため、品質管理エンジニアがガラスビーズの製品特性を詳細に分析し、確実な品質評価を行うために最適なツールとなります。
BeVision S1の測定結果は、粒度と形状の関連性を示す散布図として表示され、不規則な形状を持つ粒子の分布を視覚的に比較できます。これにより、サンプルAとサンプルBの形状分布の違い、不規則性の濃度、さらにはそれらが製品品質に与える影響を的確に評価することができます。これにより、ガラスビーズ製品の特性を詳細に理解し、品質保証のプロセスを強化することが可能になります。
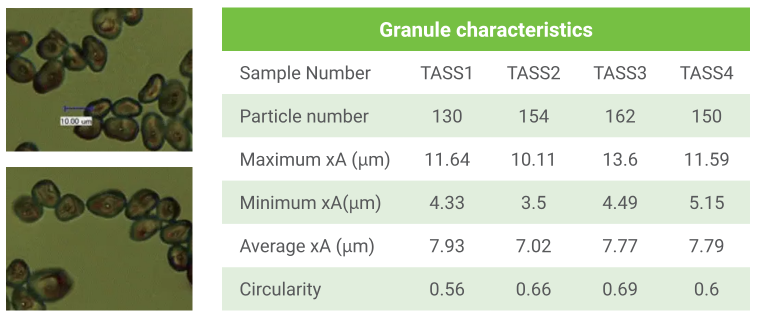
トレクリウス・アフリカーナ(Treculia africana)種の澱粉
生物学研究における他の微粒子と同様に、異なる植物源から得られた澱粉顆粒は、特徴的な形状、サイズ、そして構造を示します。このため、BeVision S1は、粒子の総数をカウントし、同時にそのサイズと形状を自動的に分析する柔軟な方法を提供します。例えば、イバダン大学とグリンドウア大学の研究者は、トレクリウス・アフリカーナ種の種子澱粉顆粒の形状とサイズを分析するためにBeVision S1を活用し、澱粉製造に関する新たな洞察を得ることができました。
BeVision S1は、粒子の正確な測定を提供し、研究者が異なる植物由来の澱粉粒子の特性を深く理解できるようサポートします。また、形状分布やサイズ分析を通じて、製造工程の最適化や新たな材料開発への応用が期待できます。
6. 応用分野

Citations
- Bettersizer 2600
Functional redundancy as an indicator for evaluating functional diversity of macrobenthos under the mussel raft farm near Gouqi Island
DOI: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2023.740024 Read ArticleZhejiang Ocean University | 2024Biological traits analysis (BTA) helps to evaluate the effects of different environmental variables on the traits-based functional composition of macrobenthos. However, research on functional traits of macrobenthos under mussel farming is limited. We investigated the spatial and temporal response of the benthic system in terms of taxonomic and functional diversity to environmental variables of farming and natural stressors resulting from suspended mussel farming near Gouqi Island of eastern China Sea. The functional traits of macrobenthic assemblages under mussel farming were characterized by “medium adult body size”, “vermiform body form”, “high flexibility”, “infauna”, “semi-motile”, “gonochoristic”, “surface deposit-feeders”, “carnivores”, “semi-motile burrowers”, and “tube-dwellers”. Functional redundancy was stable in response to mussel farming stresses among seasons, whereas species diversity showed efficient to evaluate natural variables. Functional diversity was significantly affected by farming stressors rather than natural variables, Further analysis using multivariate methods together with continuous monitoring were highlighted to evaluate the impacts of mussel farming. Our results reinforce the importance of macrobenthic species and functional traits analysis to evaluate human stresses driven impacts in offshore ecosystems. By analysing the environmental variables with different sources, independently, we concluded the main effects of human pressures on macrobenthic community. Such distinction could be particularly effective to isolate variable environmental descriptors and evaluate their effects on functional diversity, making the current approach promising for the evaluation of ecological effects of anthropogenic stressors in aquaculture areas. - Bettersizer 2600
Degradation characteristics and utilization strategies of a covalent bonded resin-based solid amine during capturing CO2 from flue gas
DOI: 10.1016/j.seppur.2023.125621 Read ArticleChina University of Petroleum | 2024In this study, various types of degradation as well as attrition which are possibly encountered in a circulating fluidized bed temperature swing adsorption (CFB-TSA) process, were conducted experimentally to evaluate the stability of a resin-based solid amine sorbent. Other characterizations methods, such as elemental analysis (EA), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) etc. were applied to further reveal the degradation mechanisms. The results showed that thermal degradation occurs from 140–160 °C due to the decomposition of amine group. The CO2-induced degradation occurs from a higher temperature of 160–180 °C accompanied by the production of urea. Hydrothermal stability is good below 130 °C, but the ionic impurities in steam crystalized on particle surface can accelerate the degradation. Oxidative degradation is the most harmful, which starts at a lower temperature of 70–80 °C with the formation of aldehyde. The existence of H2O in atmosphere can alleviate the oxidative and CO2-induced degradations. The employed sorbent has a very low attrition index of 0.05, which is 1–2 orders lower than typical commercial fluidized bed catalysts. Based on the results of stability evaluation, some design suggestions for proper utilization of this sorbent or other similar resin-based sorbents have been provided in an industrial CFB-TSA process.
- Bettersizer 2600
De-branching of starch molecules enhanced the complexation with chitosan and its potential utilization for delivering hydrophobic compounds
DOI: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2023.109498 Read ArticleShihezi University | 2024The current study aimed to prepare the complexes between debranched-waxy corn starch and chitosan polymers (DBS-CS), and then investigated their corresponding structural characteristics, rheological property and potent application in Pickering emulsion. The results indicated that the existence of chitosan significantly inhibited starch short-range molecular rearrangement for all DBS-CS samples, which was manipulated by both debranching treatment and chitosan content. Interestingly, this is the first study to reveal that the outstanding peak at 1.8 ppm in 1H NMR spectrum for sample DBS-CS was gradually shifted towards a lower-field region following an increased chitosan content. Moreover, the debranching treatment shifted the crystallinity pattern from A-type to B-type and the relative crystallinity of DBS-CS decreased gradually with the increased content of CS. All samples had a pseudoplastic fluid and shear-thinning behavior with an enhanced shear resistance following the complexation. The DBS-CS was applied in a Pickering emulsion for showing a greater emulsifying stability and a lower gel strength than native NS-CS prepared emulsion. Importantly, the encapsulation ability of curcumin in the DBS-CS emulsion was significantly improved, followed by an increase of 15.45% for its corresponding bioavailability compared to the control. Therefore, this study might highlight a potential carrier for delivering the bioactive substances in a green pattern. - Bettersizer 2600
Heat-induced aggregation behavior of wheat gluten after adding citrus pectin with different esterification degree
DOI: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2023.109420 Read ArticleGansu Agricultural University | 2024Wheat gluten aggregation during heat treatment is beneficial to the final quality of gluten-based products. Exogenous pectin can affect gluten aggregation. However, the effect of pectin with different degrees of esterification on the heat-induced aggregation behavior of gluten and its possible mechanism are still unclear. Thus, the heat-induced aggregation behavior of gluten after adding pectin with different esterification degree was studied in this study. When the temperature was raised from 25 °C to 95 °C, pectin affected gluten aggregation and was related to the degree of esterification. Specifically, the results of rheological properties and particle size indicated that low-ester pectin improved the viscoelasticity of gluten and promoted gluten aggregation. Thermal properties revealed that enthalpy of gluten added with low-ester pectin (37%) increased from 92.96 J/g to 95.40 J/g during heating process. Structurally, the fluorescence intensity and surface hydrophobicity of gluten added with low-ester pectin (37%) were lower than those added with high-ester pectin (73%). In addition, low-ester pectin (37%) significantly increased the disulfide bond content (from 15.31 μmol/g to 18.06 μmol/g) and maintained β-sheet content of gluten compared with gluten alone at 95 °C, indicating that low-ester pectin was more likely to induce gluten aggregation. However, scanning electron microscope showed that the gluten added with low-ester pectin (46%) exhibited a denser network structure at 95 °C than that added with low-ester pectin (37%). These results will provide a theoretical base for the regulation of gluten aggregation and the quality of gluten-based products by pectin with different esterification degree.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 84

















